Weekly Outlook (18/03/2019 to 24/03/2019)
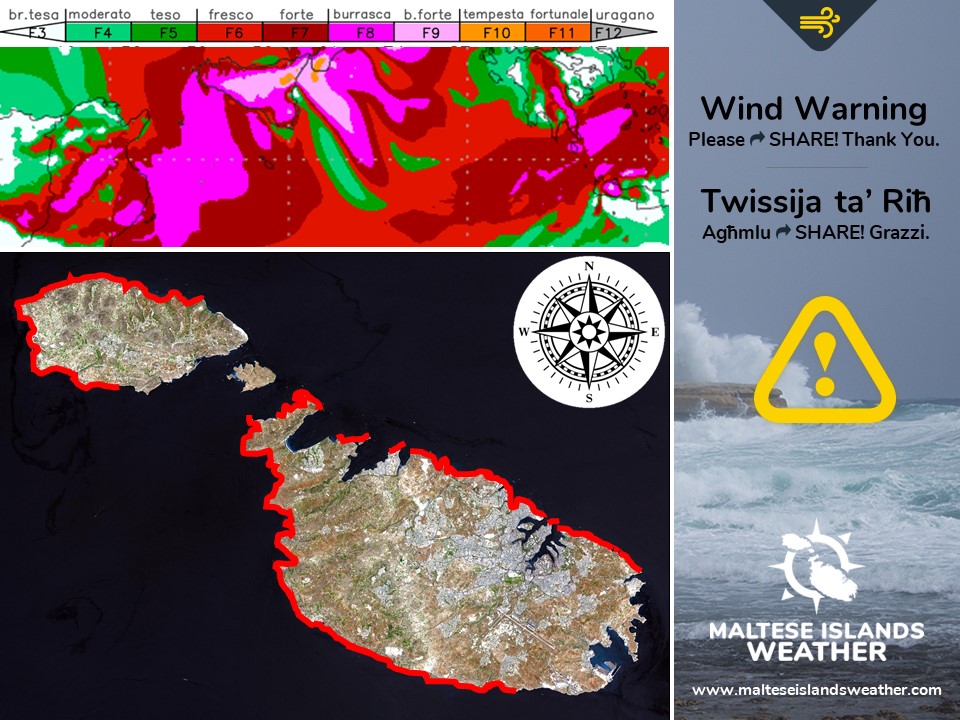
As promised, the Maltese Islands enjoyed a weekend of uninterrupted bright sunshine. High pressure which has taken hold of the central Mediterranean will prevail till late on Monday 18/03. This means another day of gloriously warm sunshine to start off the week. This high pressure will retreat south on Tuesday 19/03, however, when an area of low pressure will develop over the central Mediterranean. This will mark the brief return of wintry weather; with rain/hail showers, strong Northeasterly winds and cooler temperatures returning to the Maltese Islands. The worst of it all is expected on Thursday 21/03, when the Northeast wind should reach Force 7/8 across exposed areas of our country. This state of affairs will prevail till Friday 22/03. High pressure will once again take hold of the central Mediterranean over the weekend, promising another weekend of bright sunshine. Air temperatures will also rise again, as southerly winds blow warm air from over north Africa towards our region. This is expected to be the third heat spell of the season.
Taking a look at the weather across the Maltese Islands over the coming week, the average maximum temperature will be around 19°C, with a high for the week peaking at 22°C expected on Monday 18/03. Meanwhile, the average minimum temperature will be 12°C, dipping to its lowest in the mornings of Saturday 23/03 and Sunday 24/03 at 11°C. This week will see some significant precipitation, with rain/hail showers expected from late on Tuesday 19/03 till early on Friday 22/03. Thursday 21/03 will be the wettest, with over 10 mm. Winds are expected to be strong to very strong from the East to East Northeast on Wednesday 20/03, Thursday 21/03 and Friday 22/03, with the strongest expected on Thursday 21/03. The rest of the days will be characterised by a light breeze from the West.